Difference between revisions of "Sigma"
(→HOW SIGMA PERTAINS to the BELL CURVE) |
(→1 SIGMA) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
=== 1 SIGMA === | === 1 SIGMA === | ||
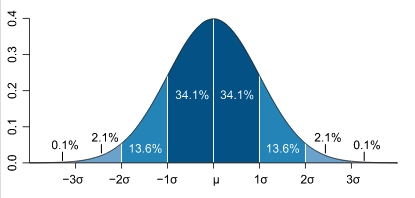
| − | If someone says that an error is 1 sigma, then that person is referring to the greatest possible error in between the lines marked with -1 | + | If someone says that an error is 1 sigma, then that person is referring to the greatest possible error in between the lines marked with - 1 sigma to + 1 sigma in the bell curve (see the curve above). Add the percentages of the two regions under the bell and you will |
Now three sigma is 3* the standard deviation, which statistically mean that 99.73% of the time a measurement is made it will be within 3*the standard deviation of the actual value. It is thus a way to compare how good the measurement method is. | Now three sigma is 3* the standard deviation, which statistically mean that 99.73% of the time a measurement is made it will be within 3*the standard deviation of the actual value. It is thus a way to compare how good the measurement method is. | ||
In similar ways 2 sigma means within 95% of the actual value and 6 sigma means as close to always as is resonable to ever need. | In similar ways 2 sigma means within 95% of the actual value and 6 sigma means as close to always as is resonable to ever need. | ||
Revision as of 23:53, 3 October 2011
|
Most have heard of the "bell curve" in mathematics. This is the shape that describes the probability that a given percentage of measurements will fall within a certain region under a standard bell curve. This shape is found in nature - so its one that mathematicians use often. This shape of the standard bell curve is called "Normal Distribution" or "Gausian Distribution." |
HOW SIGMA PERTAINS to the BELL CURVE
A statistical measurement called "standard deviation" is also referred to as "sigma" on the horizontal axis of a bell curve. Basically, this is a measurement of how much the measurements vary from the center value by a distance of a value called "sigma" on either side of the center of the curve.
1 SIGMA
If someone says that an error is 1 sigma, then that person is referring to the greatest possible error in between the lines marked with - 1 sigma to + 1 sigma in the bell curve (see the curve above). Add the percentages of the two regions under the bell and you will
Now three sigma is 3* the standard deviation, which statistically mean that 99.73% of the time a measurement is made it will be within 3*the standard deviation of the actual value. It is thus a way to compare how good the measurement method is.
In similar ways 2 sigma means within 95% of the actual value and 6 sigma means as close to always as is resonable to ever need.