VTube-LASER End Point Deviations
|
|
Contents |
Three Main End Point Deviations
|
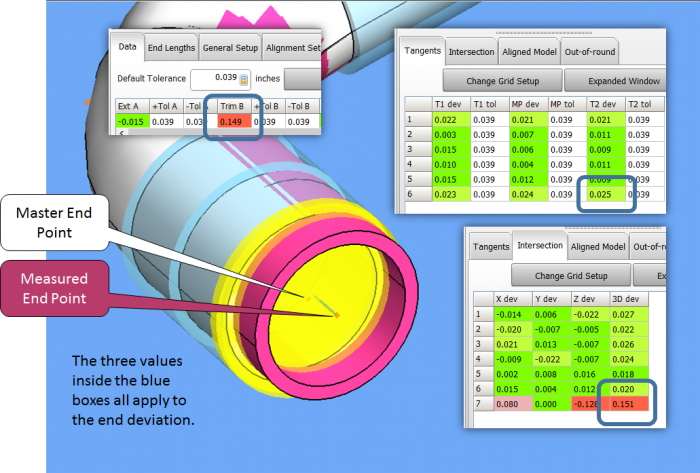
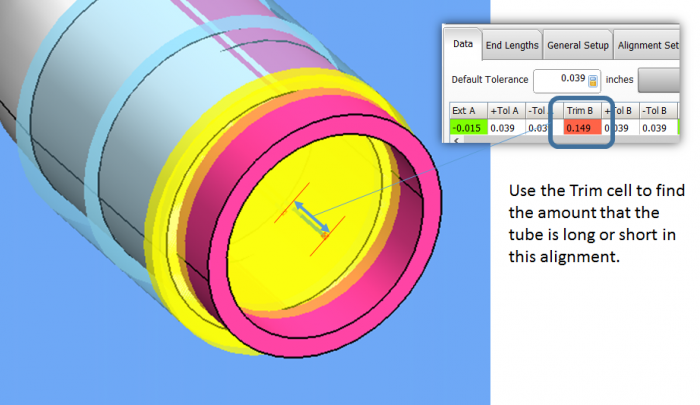
There are three main end point deviation values calculated during an alignment of the MEASURED to the MASTER tube. |
END LENGTH Deviations
|
The end length deviations are found at the top of the Inspection menu.
|
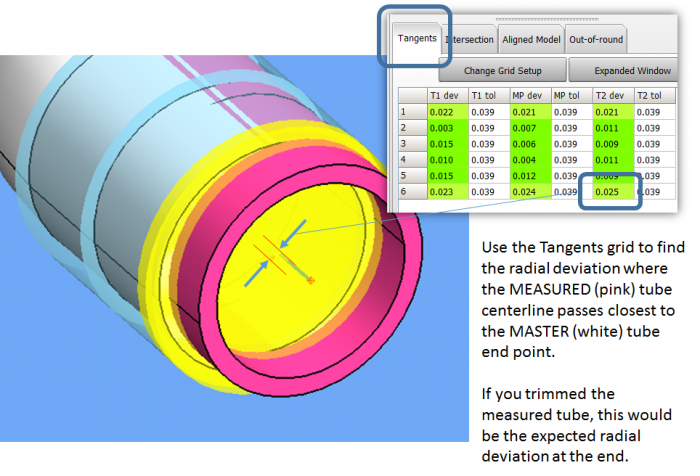
AFTER-TRIM Deviations
|
These are found in the first T1 value and the last T2 value in the Tangents grid.
|
How to Understand the End Point Deviations
Automatic Internal Trimming of End Points for Shape
|
Even though the end points are not tangents, we can still use them in the chart because they qualify the part the same way that tangent points do. |
Untrimmed End Points for Lengths
|
However, the end length is 90.2mm too long. In this application, the customer bent the part 90mm too long on purpose in order to give the bend arm clamp die enough material on the first straight to grip. Notice that, even though the part is significantly too long, the BEST FIT algorithm didn't use the actual measured end point in the alignment. The alignment was based on the trimmed point on the measured centerline that was nearest the master end point. So, in this case the part shape in space is qualified - but it needs trimming by 90.2mm to also qualify the end length (another critical qualifier). |
Typical Industry Tangent Point Tolerances
|
In working with thousands of customers over the past few decades, we've seen some trends in accepted envelope deviation tolerances. Here are what we commonly see: Aerospace and Automative Fluid Lines
Automotive Exhaust Pipes
Shipbuilding
HVAC
Structural Tubes (Frames)
Tighter TolerancesSometimes customers will required +/-0.75 mm - but this is very rare. We've never seen tube shapes that must be qualified with a deviation tolerance of less than +/- 0.75 mm. |
Other Pages
- See also VTube Intersection Point Tolerances
- Back to VTube-LASER